learning, development, azure, dotnet, conference, documentation
The Future of Web Development with ASP.NET Core & Blazor
Session Overview
Session Code: BRK122
Event: Microsoft Build 2025
Date: May 19-22, 2025
Speakers: - Daniel Roth - Principal Product Manager, ASP.NET Core & Blazor - Mike Kistler - Principal Product Manager, ASP.NET Core Team (Backend APIs focus) Recordings: - https://build.microsoft.com/en-US/sessions/BRK122?source=sessions
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
This session provided an in-depth look at the future of web development with ASP.NET Core and Blazor, focusing on the upcoming .NET 10 release.
The speakers highlighted four key areas of investment: security enhancements, observability improvements, performance optimizations, and addressing long-standing pain points in the framework.
Key Statistics and Impact
- 2+ million developers use ASP.NET Core monthly
- ASP.NET Core powers major Microsoft services: Microsoft 365, Bing, Teams, Copilot, Xbox, and Azure services
- Performance leadership: 3x faster than Express.js, 5x faster than Go’s Gin framework in TechEmpower benchmarks
- Continuous performance improvements with each release
Major Focus Areas for .NET 10
The .NET 10 release focuses on four key areas of investment to enhance the developer experience and application capabilities:
- Security Enhancements - Implement modern authentication patterns with passkey support and improved OAuth 2.0 token management
- App Observability and Diagnostics - Provide comprehensive metrics collection and advanced diagnostic tools for better application monitoring
- Performance Improvements - Optimize memory management, JSON processing, and startup times for faster, more efficient applications
- Pain Points and Developer Experience - Address long-standing framework limitations and improve developer productivity through better tooling
1. Security Enhancements
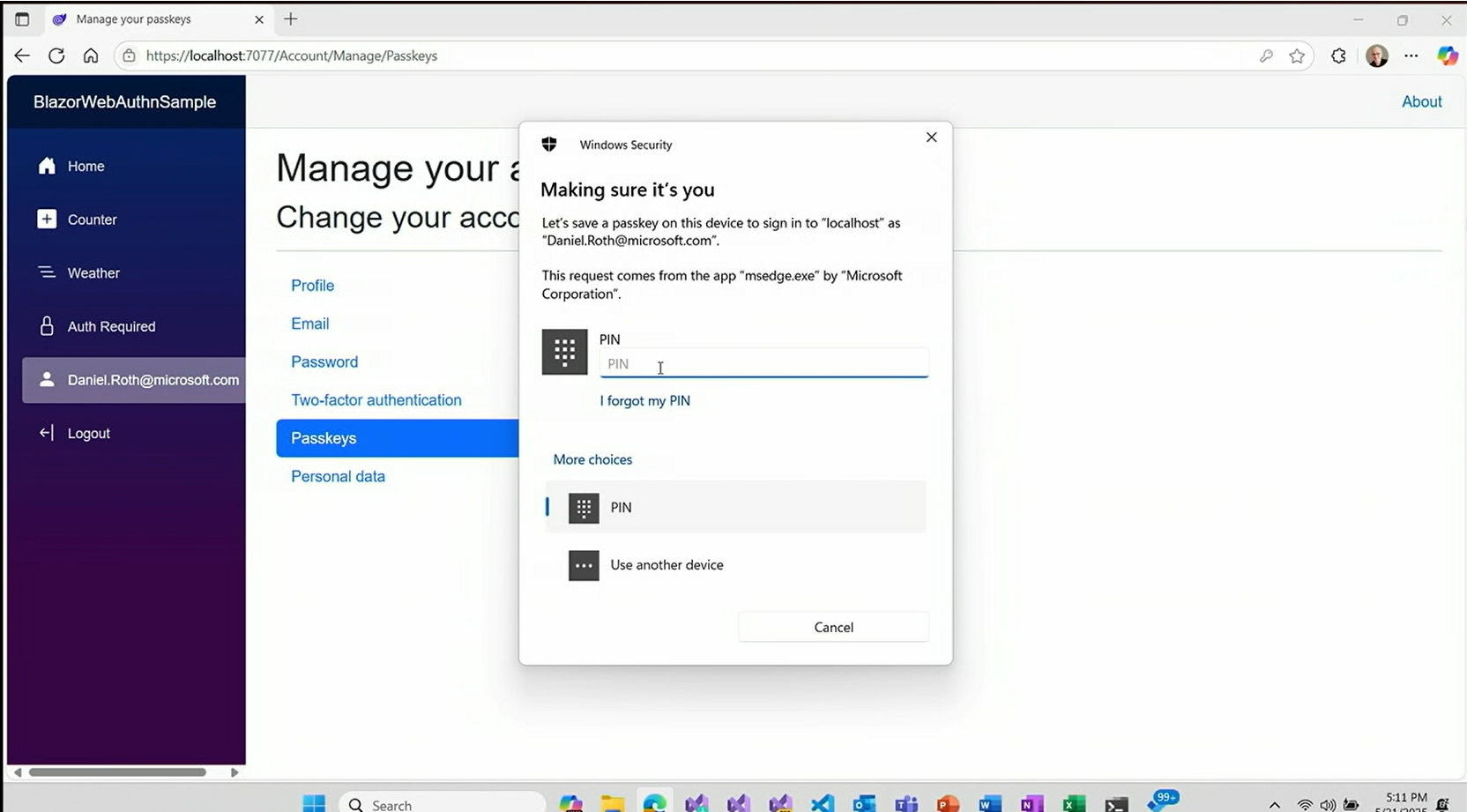
Passkey Authentication Support
- Revolutionary change: Complete replacement of traditional passwords with cryptographic credentials
- Implementation: Public-private key pairs with secure storage in authenticators
- Benefits:
- Phishing-resistant authentication
- Application-scoped credentials (no cross-application sharing)
- Seamless user experience
- Integration: Built into ASP.NET Core Identity framework
- Based on: FIDO2.NET library foundation
- Template support: Available in project templates and existing project migration tools
OAuth 2.0 Refresh Tokens
- Automatic token refresh: Seamless renewal without user interaction
- Security improvement: Shorter token lifespans reduce exposure risk
- Enhanced UX: No interruption to user workflows
Developer Experience Improvements
- Scaffolding tools: New dotnet scaffold command for authentication patterns
- Cross-platform support: Interactive command-line experience
- Multiple auth scenarios:
- ASP.NET Core Identity endpoints
- Entra ID authentication
- Blazor Hybrid and .NET MAUI apps
- Documentation overhaul: Scenario-based tutorials and video content
2. App Observability and Diagnostics
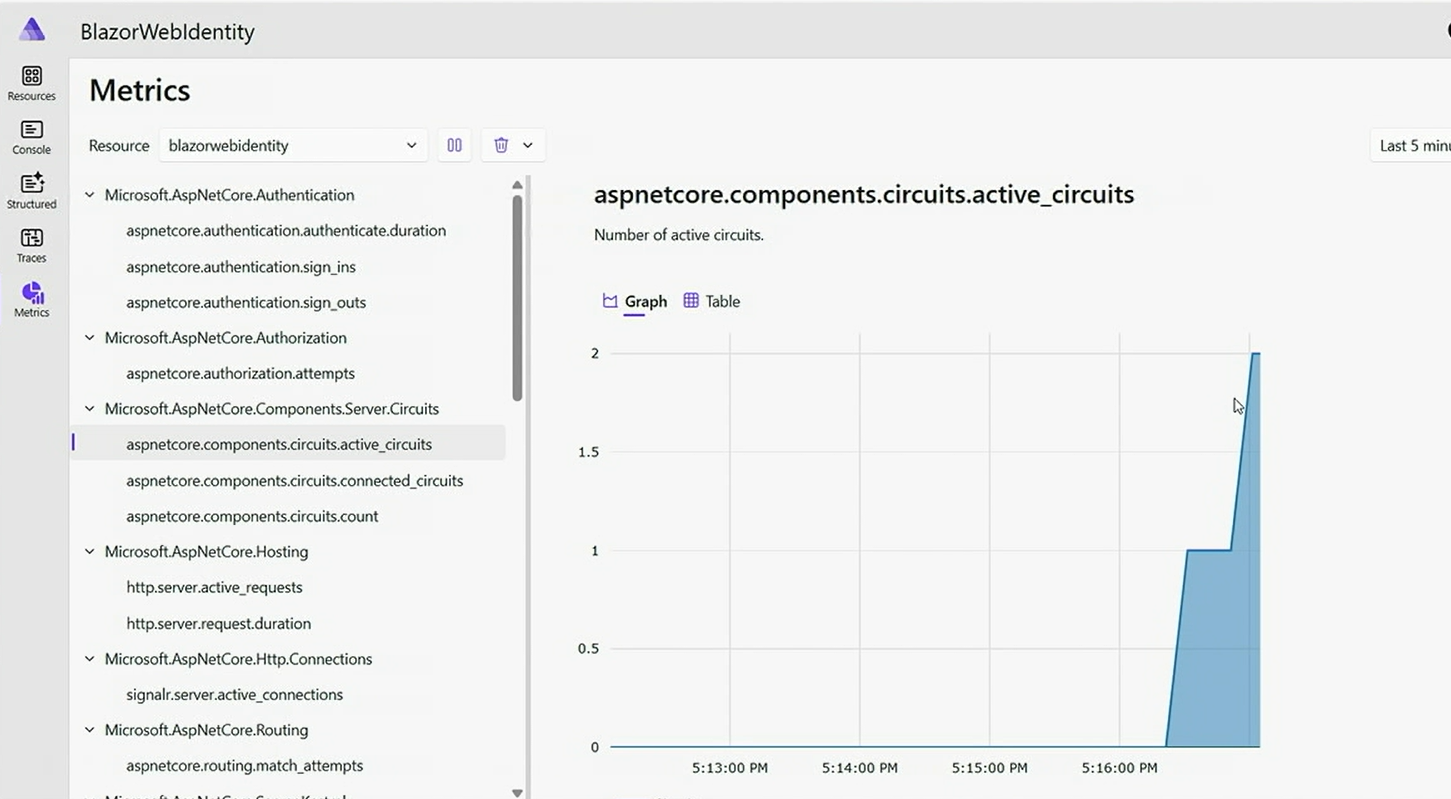
Enhanced Metrics Collection
- Kestrel memory pool metrics: Memory usage tracking and optimization
- Authentication/Authorization metrics: Security operation monitoring
- Blazor-specific metrics:
- Circuit count and status tracking
- Connection state monitoring
- Interactive rendering metrics
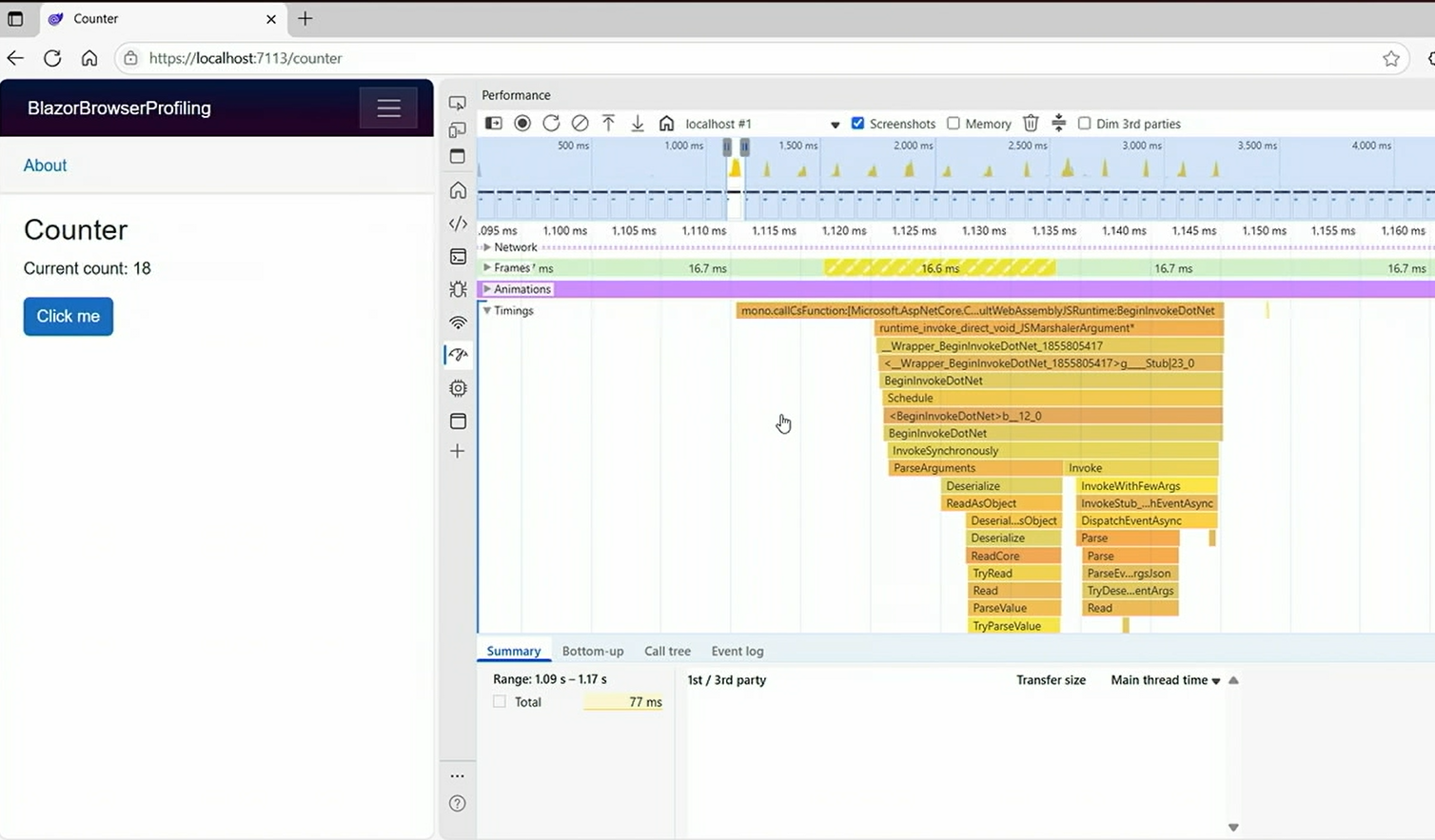
Blazor WebAssembly Diagnostics
- Browser DevTools integration: Performance profiling capabilities
- Extractable diagnostics:
- CPU sampling and analysis
- Performance counter collection
- GC dump generation for memory analysis
- Visual Studio integration: Complete diagnostic workflow
OpenTelemetry Integration
- Native instrumentation: Built-in semantic conventions
- No additional packages required: Streamlined setup process
- Identity model logging: JWT token validation visibility
3. Performance Improvements
Memory Management Optimizations
- Kestrel memory pool evolution: Dynamic memory release capabilities
- Real-world validation: Tested in Azure App Service at billion-request scale
- Measurable impact: Demonstrated memory reduction in production environments
- Scalability benefits: Lower idle costs and smarter resource utilization
JSON Processing Enhancements
- PipeReader support: System.Text.Json deserialization improvements
- Continuation from .NET 9: Completing the serialization/deserialization optimization cycle
- API performance: Significant speed improvements for data processing
Blazor WebAssembly Startup Optimization
- Framework script optimization: Static web asset treatment for caching
- Fingerprinting: Unique file names for aggressive browser caching
- Pre-compression: Gzip (development) and Brotli (production) compression
- Preloading support: Reduced cascade request delays
- Standalone app support: Build-time placeholder replacement system
4. Pain Points and Developer Experience
Minimal API Enhancements
- Automatic validation: Data annotation support (previously controller-only)
- Custom validation attributes: Extensible validation system
- Object-level validation: Cross-property validation support
- Server-sent events: Native support for AI application patterns
OpenAPI Generation Improvements
- OpenAPI 3.1 support: Latest standard implementation
- XML documentation integration: Automatic metadata extraction
- YAML output support: Alternative to JSON format
- Build-time generation: Performance and deployment optimizations
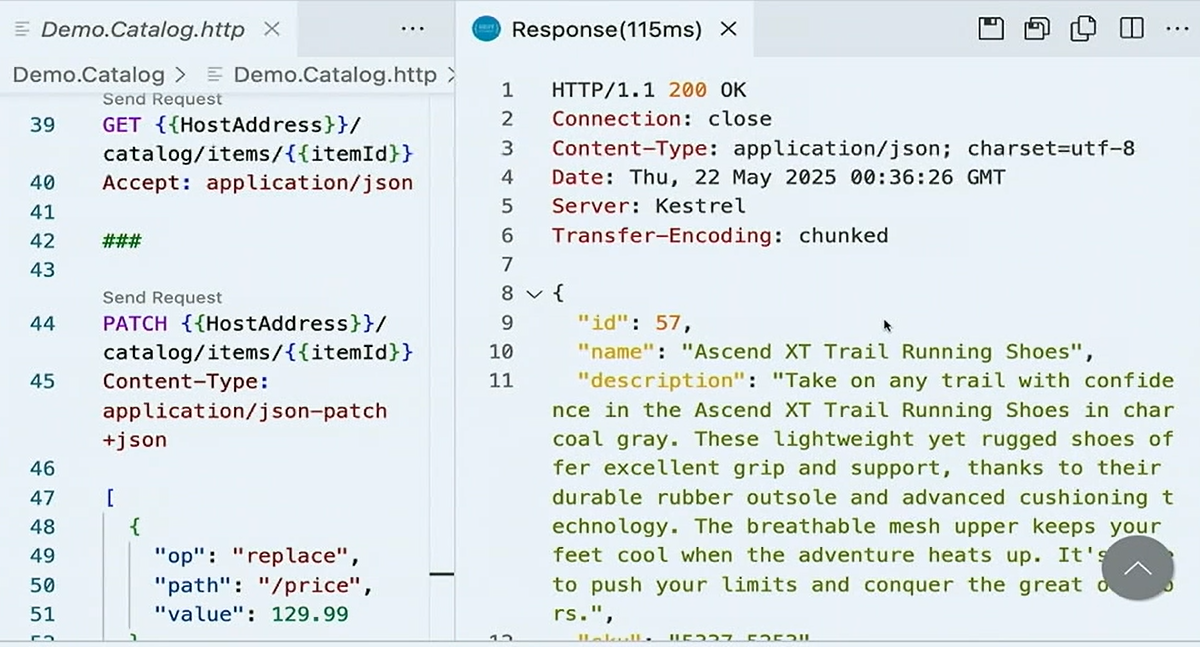
JSON Patch with System.Text.Json
- Modern JSON library support: Eliminates Newtonsoft.Json dependency
- Concurrent operation safety: Test operations for data consistency
- Error handling: Comprehensive validation and error reporting
Blazor Frontend Improvements
- State persistence: Declarative attribute-based model
- Circuit resilience: Automatic state preservation during disconnections
- Scalability controls: Manual circuit management APIs
- QuikGrid enhancements:
- Row styling based on data
- Column option control
- Entity Framework integration improvements
JavaScript Interop Advancements
- Direct constructor calls: Simplified JavaScript integration
- Property access: Enhanced JavaScript object manipulation
- Callback improvements: Streamlined event handling
- Standalone .NET libraries: JavaScript app integration capabilities
Testing Infrastructure
- Web Application Factory + Kestrel: Real server testing capabilities
- Playwright/Selenium integration: Full browser automation support
- End-to-end testing: Complete application pipeline validation
Technical Implementation Details
Passkey Authentication Demo
The session demonstrated a complete passkey implementation showing: - User account setup with passkey registration - Windows Hello integration for biometric authentication - Seamless login experience without passwords - Multi-device support capabilities
Performance Diagnostics Demo
Showcased advanced diagnostic capabilities: - Real-time performance profiling in browser DevTools - Memory dump analysis in Visual Studio - CPU sampling and performance counter extraction - Integration with existing development workflows
JSON Patch Implementation
Demonstrated practical usage: - Product catalog price updates - Concurrent operation handling with test operations - Error handling and validation feedback - Database transaction safety
AI Integration and Modern Development
.NET Platform AI Capabilities
- Microsoft.Extensions.AI: Generative AI integration primitives
- Evaluations library: AI application quality and safety assessment
- VectorData: Semantic search and embedding management
- AI project templates: Ready-to-use chat interface foundations
- C# Model Context Protocol SDK: Extensible AI application development
- Semantic Kernel: Multi-agent workflow orchestration
.NET Aspire Integration
- Cloud-native development: Seamless AI and cloud service integration
- Existing application compatibility: Add to any ASP.NET Core app
- Built-in best practices: OpenTelemetry, health checks, resiliency
- Local development: Complete application orchestration
- Service integration: Redis, PostgreSQL, AI services
- Observability: Integrated dashboard for logs, metrics, and traces
- Flexible deployment: Any cloud or hosting environment
Development Best Practices and Recommendations
Security-First Development
- Implement passkey authentication for modern security
- Use OAuth 2.0 refresh tokens for better token management
- Leverage scaffolding tools for consistent authentication patterns
- Follow updated documentation for identity implementation
Performance Optimization
- Utilize new Kestrel memory pool features for better resource management
- Implement System.Text.Json with PipeReader for high-performance APIs
- Optimize Blazor WebAssembly apps with new startup improvements
- Monitor applications with enhanced metrics collection
Modern Architecture Patterns
- Adopt minimal APIs for new web applications
- Implement proper validation with data annotations
- Use OpenAPI 3.1 for comprehensive API documentation
- Leverage JSON Patch for efficient data updates
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Implement comprehensive testing with Web Application Factory + Kestrel
- Use automated browser testing for complete UI validation
- Leverage enhanced diagnostic tools for performance analysis
- Monitor application health with improved observability features
Future Roadmap and Timeline
.NET 10 Development Timeline
- Current Status: Preview releases available
- Target Release: .NET Conf 2025 (November)
- Feature Availability: Gradual rollout through preview releases
- Migration Path: Existing applications can upgrade incrementally
Preview Release Schedule
- Preview 4: Already available with validation and JSON Patch support
- Upcoming Previews: Additional features and refinements
- Release Candidate: Feature-complete version before final release
- Final Release: November 2025 at .NET Conf
Migration and Adoption Strategy
For Existing Applications
- Incremental adoption: Add new features without breaking changes
- Backward compatibility: Existing code continues to work
- Migration tools: Automated assistance for complex changes
- Documentation: Comprehensive upgrade guides and tutorials
For New Applications
- Modern templates: Latest patterns and best practices included
- Scaffolding tools: Automated setup for common scenarios
- Integration guidance: Clear paths for AI and cloud services
- Performance optimizations: Built-in from the start
Conclusion
The future of web development with ASP.NET Core and Blazor is focused on developer productivity, security, performance, and modern application patterns. .NET 10 represents a significant evolution in the platform, addressing long-standing pain points while introducing cutting-edge features for AI-powered and cloud-native applications.
The emphasis on security through passkey authentication, enhanced observability through comprehensive metrics, performance improvements through memory optimization, and developer experience improvements through better tooling positions ASP.NET Core as a leading platform for modern web development.
References
Official Documentation and Resources
- .NET 10 What’s New Documentation
- Comprehensive overview of all new features in .NET 10
- Relevant for understanding the complete scope of changes beyond ASP.NET Core
- ASP.NET Core Official Documentation
- Primary resource for ASP.NET Core development
- Essential for implementing the concepts discussed in the session
- Blazor Documentation
- Detailed guidance on Blazor development patterns
- Critical for understanding the frontend improvements discussed
- .NET 10 Preview Downloads
- Access to preview releases mentioned in the session
- Allows developers to try new features before final release
- Build25 BRK122 Demos
- Official demo code and samples from the Build 2025 BRK122 session
- Hands-on examples of passkey authentication, observability features, and performance improvements
- Complete implementation samples for all major features discussed in the session
Security and Authentication
- 01. Passkey Authentication Information
- Comprehensive guide to passkey authentication technology
- Detailed explanation of how passkeys work and their security benefits
- Implementation guidance for ASP.NET Core applications
- FIDO Alliance - WebAuthn Specification
- Technical specification for Web Authentication API
- Essential for understanding passkey implementation details
- Microsoft Identity Platform Documentation
- Comprehensive guide for identity and authentication patterns
- Relevant for understanding OAuth 2.0 and Entra ID integration
- ASP.NET Core Security Best Practices
- Security guidelines and best practices
- Important for implementing the security features discussed
Performance and Diagnostics
- OpenTelemetry .NET Documentation
- Observability and telemetry implementation guidance
- Relevant for understanding the diagnostic improvements
- Kestrel Web Server Documentation
- Detailed information about Kestrel configuration and optimization
- Essential for understanding memory pool improvements
- System.Text.Json Documentation
- JSON processing optimization and configuration
- Critical for understanding performance improvements
AI and Modern Development
- .NET Aspire Documentation
- Cloud-native application development with .NET
- Relevant for understanding modern application architecture
- Microsoft.Extensions.AI Documentation
- AI integration patterns and libraries
- Important for understanding AI-powered application development
- Semantic Kernel Documentation
- Multi-agent AI workflow orchestration
- Relevant for complex AI application scenarios
Testing and Quality Assurance
- ASP.NET Core Testing Documentation
- Comprehensive testing strategies and tools
- Essential for understanding the testing improvements
- Playwright for .NET
- Browser automation framework
- Relevant for the automated testing capabilities demonstrated
API Development
- OpenAPI Specification
- API documentation standards
- Important for understanding OpenAPI 3.1 improvements
- JSON Patch RFC 6902
- JSON Patch operation specification
- Essential for understanding the JSON Patch implementation
Community and Learning
- .NET Community Blog
- Regular updates and deep dives into .NET features
- Valuable for staying current with platform developments
- ASP.NET Core GitHub Repository
- Source code and issue tracking
- Important for understanding implementation details and contributing
- .NET Roadmap
- Long-term platform planning and feature timeline
- Essential for understanding future development directions
- .NET Conf 2025
- Annual conference for .NET release celebrations
- Important for staying informed about major releases and announcements
Performance Benchmarking
- TechEmpower Framework Benchmarks
- Independent web framework performance comparisons
- Relevant for understanding ASP.NET Core performance claims
- ASP.NET Core Performance Best Practices
- Optimization guidelines and recommendations
- Essential for implementing high-performance applications
APPENDIXES
APPENDIX 01: Passkeys in Blazor Hybrid and .NET MAUI Applications
What are Blazor Hybrid and .NET MAUI Apps?
Blazor Hybrid
- Native desktop/mobile apps that host Blazor web components inside a WebView
- Combines: Native app shell + Blazor UI components
- Platforms: Windows (WPF/WinUI), macOS, iOS, Android
- Architecture: Native app container → WebView → Blazor components
.NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI)
- Cross-platform framework for native mobile and desktop apps
- Single codebase that runs on Windows, macOS, iOS, Android
- Can include: Blazor Hybrid components within native MAUI apps
- Architecture: Native app framework + optional Blazor UI components
Passkey Authentication in Hybrid Applications
Authentication Architecture Overview
Traditional Web App: Browser → Web Server → Authentication Hybrid App: Native App → WebView/Native Auth → Web Services + Local Storage
How Passkeys Work in Hybrid Context
1. Platform-Specific Authentication
Windows (WinUI/WPF):
// Uses Windows Hello integration
var result = await WebAuthenticationBroker.AuthenticateAsync(
WebAuthenticationOptions.None,
passKeyAuthUri);iOS (.NET MAUI):
// Uses Touch ID/Face ID through AuthenticationServices
var authService = new ASAuthorizationController();
await authService.PerformRequestsAsync();Android (.NET MAUI):
// Uses Android Biometric APIs
var biometricPrompt = new BiometricPrompt();
await biometricPrompt.AuthenticateAsync();2. Identity Flow Across Application Parts
Multi-Part Authentication Flow:
- Native Authentication: User authenticates with device biometrics
- Passkey Generation: Platform creates cryptographic credentials
- Token Exchange: Native app receives authentication tokens
- WebView Communication: Tokens passed to Blazor components
- API Access: Both native and web parts use shared identity
3. Cross-Component Identity Sharing
Shared Identity Store:
// Identity service shared between native and Blazor parts
public interface IIdentityService
{
Task<AuthResult> AuthenticateWithPasskeyAsync();
Task<string> GetAccessTokenAsync();
Task ShareIdentityWithWebViewAsync(string token);
}Token Sharing Pattern:
// Native part authenticates
var authResult = await identityService.AuthenticateWithPasskeyAsync();
// Share with Blazor WebView
await webView.InvokeScriptAsync("setAuthToken", authResult.Token);
// Blazor component receives identity
window.setAuthToken = (token) => {
// Store for API calls
localStorage.setItem('authToken', token);
};Technical Implementation Considerations
Challenge-Response Flow in Hybrid Apps
Native Passkey Flow: 1. App requests authentication → Platform prompts for biometric 2. Platform generates signature → Using device-stored private key 3. App receives credential → Cryptographic proof of identity 4. App exchanges with server → Gets JWT/session tokens 5. Tokens shared internally → Between native and web components
Security Boundaries
Trust Zones: - Native App Process: Full device access, secure storage - WebView Context: Limited access, standard web security - Communication Bridge: Secure token passing between contexts
Data Protection:
// Secure storage for hybrid apps
await SecureStorage.SetAsync("passkey_token", authToken);
var token = await SecureStorage.GetAsync("passkey_token");Windows Hybrid Apps
Windows Hello Integration: - TPM-backed credentials: Hardware security module storage - Biometric authentication: Fingerprint, face, PIN - Enterprise policies: Domain-managed passkey policies
Code Example:
// Check Windows Hello availability
if (await UserConsentVerifier.CheckAvailabilityAsync() ==
UserConsentVerifierAvailability.Available)
{
var result = await UserConsentVerifier.RequestVerificationAsync(
"Authenticate with Windows Hello");
}Mobile Hybrid Apps (iOS/Android)
Platform Authentication: - iOS: Touch ID/Face ID through AuthenticationServices framework - Android: BiometricPrompt API with device biometrics - Cross-platform: .NET MAUI abstracts platform differences
Shared Implementation:
#if IOS
// iOS-specific passkey implementation
var authController = new ASAuthorizationController();
#elif ANDROID
// Android-specific biometric implementation
var biometricPrompt = new AndroidX.Biometric.BiometricPrompt();
#endifIdentity Synchronization Patterns
Hybrid App Identity Architecture
Centralized Identity Service:
public class HybridIdentityService : IIdentityService
{
private readonly ISecureStorage secureStorage;
private readonly IWebView webView;
public async Task<bool> AuthenticateAsync()
{
// 1. Platform-specific passkey auth
var passKeyResult = await PlatformAuth.AuthenticateAsync();
// 2. Exchange with server
var tokens = await ExchangePasskeyForTokens(passKeyResult);
// 3. Store securely
await secureStorage.SetAsync("access_token", tokens.AccessToken);
// 4. Share with WebView
await webView.InvokeScriptAsync("setIdentity", tokens.AccessToken);
return true;
}
}State Management Across Components
Shared State Pattern: - Native components: Access identity through dependency injection - Blazor components: Receive identity through JavaScript interop - API clients: Use shared token store for authentication headers
Best Practices for Hybrid Passkey Implementation
Security Best Practices
- Secure Token Storage: Use platform secure storage APIs
- Minimal WebView Exposure: Limit sensitive data in web context
- Token Validation: Verify tokens before cross-component sharing
- Secure Communication: Encrypt data passed between native/web parts
User Experience Best Practices
- Seamless Authentication: Single authentication for entire app
- Consistent UI: Match platform authentication patterns
- Graceful Fallback: Handle unsupported devices/features
- Clear Feedback: Show authentication status across all components
Development Best Practices
- Platform Abstraction: Use interfaces for platform-specific code
- Shared Identity Service: Centralize authentication logic
- Comprehensive Testing: Test on all target platforms
- Error Handling: Robust handling of platform-specific failures
Future Considerations
Emerging Standards
- Cross-platform passkey sync: iCloud Keychain, Google Password Manager
- Enterprise management: MDM integration for corporate devices
- Enhanced interoperability: Better cross-platform passkey sharing
Platform Evolution
- Native WebAuthn support: Direct browser API access in WebViews
- Improved security: Hardware security module integration
- Better developer tools: Unified debugging across native/web parts
APPENDIX 02: .NET 10 Scaffolding Tools - dotnet scaffold Command
Overview of dotnet scaffold Command
The dotnet scaffold command is a new CLI tool introduced in .NET 10 that automates the generation of authentication patterns and boilerplate code for ASP.NET Core applications. It provides an interactive, cross-platform experience for setting up various authentication scenarios.
Command Syntax and Basic Usage
Basic Command Structure
dotnet scaffold [subcommand] [options]Available Subcommands
identity- Scaffold ASP.NET Core Identity componentsauth- Scaffold authentication patternspasskey- Scaffold passkey authenticationentra- Scaffold Microsoft Entra ID integrationhybrid- Scaffold authentication for Blazor Hybrid/MAUI apps
Authentication Scaffolding Options
1. ASP.NET Core Identity Scaffolding
Basic Identity Setup:
dotnet scaffold identityWith Custom Options:
dotnet scaffold identity \
--use-default-ui \
--database-provider SqlServer \
--context-name ApplicationDbContext \
--output-dir Areas/IdentityAvailable Identity Options: - --use-default-ui - Use default Bootstrap UI - --database-provider - Database provider (SqlServer, SQLite, PostgreSQL, InMemory) - --context-name - DbContext class name - --output-dir - Output directory for generated files - --force - Overwrite existing files - --layout-page - Custom layout page path
2. Passkey Authentication Scaffolding
Basic Passkey Setup:
dotnet scaffold passkeyAdvanced Passkey Configuration:
dotnet scaffold passkey \
--relying-party-name "My App" \
--relying-party-id "myapp.com" \
--origins "https://myapp.com,https://localhost:5001" \
--include-fallback \
--database-provider SqlServerPasskey-Specific Options: - --relying-party-name - Display name for the application - --relying-party-id - Domain identifier for passkeys - --origins - Comma-separated list of allowed origins - --include-fallback - Include password fallback options - --user-verification - Required, preferred, or discouraged - --attestation - Attestation preference (none, indirect, direct)
3. Microsoft Entra ID Integration
Basic Entra ID Setup:
dotnet scaffold entraWith Configuration:
dotnet scaffold entra \
--tenant-id "your-tenant-id" \
--client-id "your-client-id" \
--domain "yourdomain.onmicrosoft.com" \
--callback-path "/signin-oidc" \
--include-graph-apiEntra ID Options: - --tenant-id - Azure AD tenant identifier - --client-id - Application (client) ID - --domain - Azure AD domain - --callback-path - OAuth callback path - --include-graph-api - Add Microsoft Graph API integration - --scopes - Comma-separated list of OAuth scopes
4. Hybrid Application Authentication
Blazor Hybrid/MAUI Setup:
dotnet scaffold hybridWith Platform-Specific Options:
dotnet scaffold hybrid \
--platforms "Windows,iOS,Android" \
--authentication-type "Passkey" \
--include-web-fallback \
--shared-identity-serviceHybrid-Specific Options: - --platforms - Target platforms (Windows, iOS, Android, macOS) - --authentication-type - Authentication method (Passkey, Entra, Custom) - --include-web-fallback - Include web-based authentication fallback - --shared-identity-service - Generate shared identity service interface
Interactive Mode
Starting Interactive Session
dotnet scaffold auth --interactiveInteractive Prompts: 1. Authentication Type Selection: - ASP.NET Core Identity - Passkey Authentication - Microsoft Entra ID - Custom OAuth Provider - Hybrid (Blazor/MAUI)
- Configuration Options:
- Database provider selection
- UI framework choice
- Security requirements
- Platform targets (for hybrid)
- Advanced Settings:
- Custom claim types
- Role-based authorization
- Multi-factor authentication
- Session management
Generated File Structure
Identity Scaffolding Output
Areas/
└── Identity/
├── Data/
│ └── ApplicationDbContext.cs
├── Pages/
│ ├── Account/
│ │ ├── Login.cshtml
│ │ ├── Register.cshtml
│ │ └── Logout.cshtml
│ └── Shared/
└── IdentityHostingStartup.csPasskey Scaffolding Output
Authentication/
├── Passkey/
│ ├── PasskeyService.cs
│ ├── PasskeyController.cs
│ ├── PasskeyOptions.cs
│ └── Models/
│ ├── PasskeyCredential.cs
│ └── AuthenticationResult.cs
├── Configuration/
│ └── PasskeyConfiguration.cs
└── wwwroot/
└── js/
└── passkey-auth.jsEntra ID Scaffolding Output
Authentication/
├── EntraId/
│ ├── EntraIdService.cs
│ ├── GraphApiService.cs
│ └── Models/
│ └── UserProfile.cs
├── Configuration/
│ └── EntraIdConfiguration.cs
└── Controllers/
└── AccountController.csConfiguration Files Generated
appsettings.json Updates
{
"Authentication": {
"Passkey": {
"RPDisplayName": "My Application",
"RPId": "myapp.com",
"Origins": [
"https://myapp.com",
"https://localhost:5001"
],
"UserVerification": "required",
"Attestation": "none"
},
"EntraId": {
"TenantId": "your-tenant-id",
"ClientId": "your-client-id",
"Domain": "yourdomain.onmicrosoft.com",
"CallbackPath": "/signin-oidc"
}
}
}Program.cs Modifications
// Added by scaffolding
builder.Services.AddAuthentication()
.AddPasskey(options =>
{
builder.Configuration.Bind("Authentication:Passkey", options);
})
.AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApp(options =>
{
builder.Configuration.Bind("Authentication:EntraId", options);
});
builder.Services.AddScoped<IPasskeyService, PasskeyService>();Advanced Scaffolding Scenarios
Multi-Authentication Provider Setup
dotnet scaffold auth \
--providers "Identity,Passkey,EntraId" \
--default-provider "Passkey" \
--include-provider-selection-uiEnterprise Configuration
dotnet scaffold identity \
--enterprise-features \
--include-lockout-policy \
--include-password-policy \
--include-audit-logging \
--compliance-mode "SOX,HIPAA"API-Only Authentication
dotnet scaffold auth \
--api-only \
--jwt-configuration \
--include-refresh-tokens \
--cors-origins "https://myapp.com"Customization and Extensibility
Custom Templates
dotnet scaffold identity \
--template-path "./Templates/CustomIdentity" \
--custom-user-model "ApplicationUser"Post-Scaffolding Customization
# Generate additional components
dotnet scaffold identity-components \
--components "TwoFactorAuth,ExternalLogin,PasswordRecovery"Best Practices for Scaffolding
Development Workflow
- Start with Interactive Mode for first-time setup
- Use Specific Commands for CI/CD automation
- Review Generated Code before committing
- Test All Authentication Flows after scaffolding
Security Considerations
- Update Default Secrets in generated configuration
- Review Generated Policies for compliance requirements
- Validate HTTPS Configuration in production settings
- Test Cross-Platform Compatibility for hybrid apps
Project Organization
- Use Consistent Naming across authentication components
- Separate Authentication Logic from business logic
- Document Custom Modifications to generated code
- Version Control Integration with meaningful commit messages
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Database Provider Issues
# Fix missing database provider
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
dotnet scaffold identity --database-provider SqlServer --forceMissing Dependencies
# Install required packages
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearerPlatform-Specific Problems
# iOS-specific scaffolding
dotnet scaffold hybrid --platforms iOS --fix-entitlementsFuture Enhancements
Planned Features
- AI-Assisted Scaffolding: Intelligent code generation based on project analysis
- Cloud Integration: Direct Azure/AWS service configuration
- Testing Scaffold: Automatic test generation for authentication flows
- Migration Tools: Automated upgrade paths between authentication methods
Community Extensions
- Custom Provider Templates: Community-contributed authentication providers
- Enterprise Templates: Industry-specific authentication patterns
- Integration Packages: Third-party service integrations